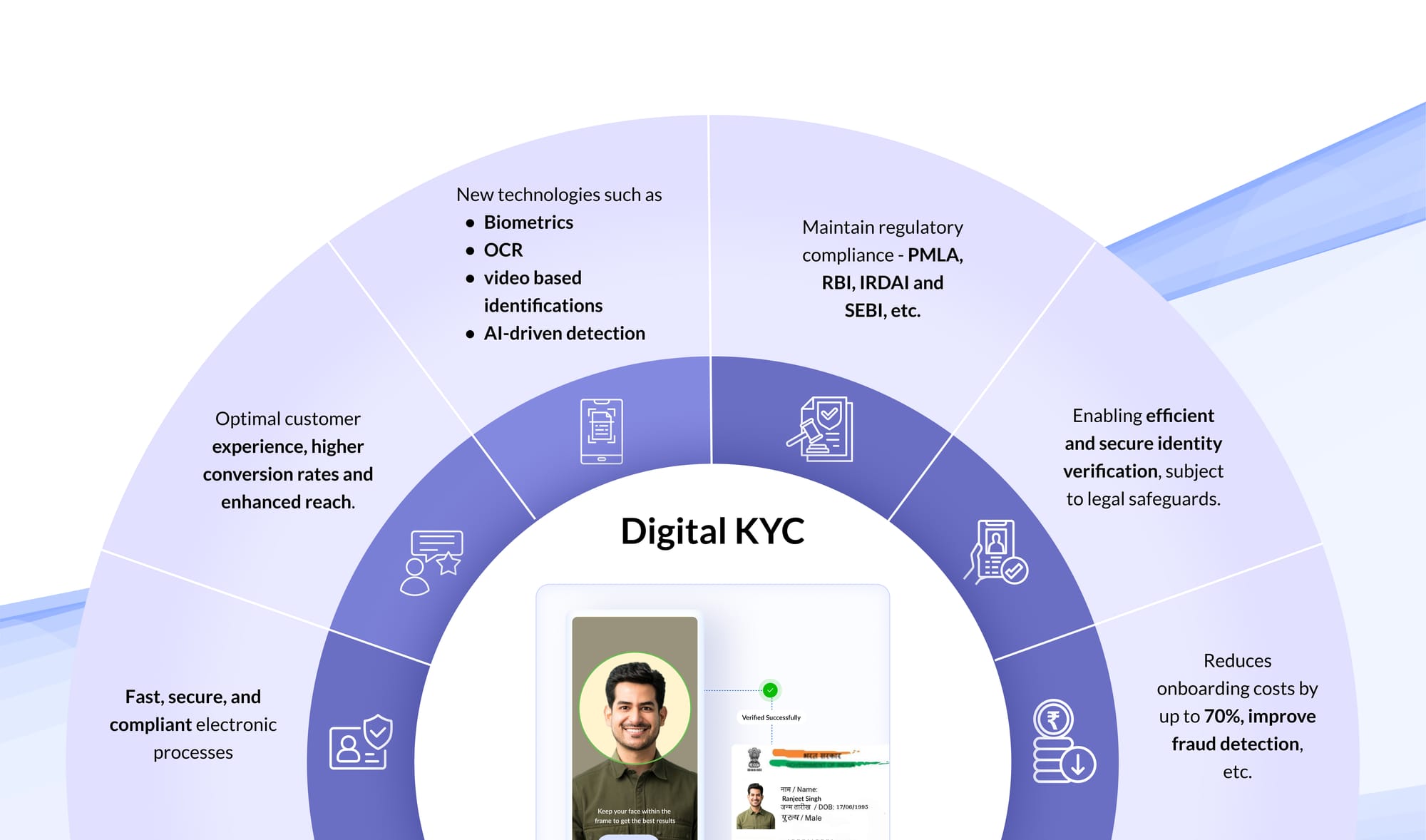
Operationalizing DPDPA Compliance with ROPA
With the release of the DPDP Rules on November 13th, 2025, one truth has become abundantly clear: effective privacy management begins with knowing exactly what personal data you process and why.
How to start DPDP Compliance Preparation?
With the release of the DPDP Rules on November 13th, 2025, one truth has become abundantly clear: effective privacy management begins with knowing exactly what personal data you process and why.
This is where Records of Processing Activities (ROPA) become not just important, but the first step in your entire DPDPA compliance program.
What is ROPA?
The Digital Personal Data Protection Act doesn't use the GDPR terminology, such as "Records of Processing Activities". However, Section 8's accountability obligations for Data Fiduciaries create an implicit requirement that's arguably more stringent. As a data fiduciary, you must demonstrate that you're processing personal data only for the specified purposes you've disclosed to Data Principals (your customers). Without comprehensive documentation, this becomes impossible.
Consider what happens when a Data Principal exercises their rights under Section 11:
- They ask what data you hold about them
- They request erasure once the purpose is fulfilled
- They withdraw consent and expect immediate action
- They nominate someone to manage their data posthumously
Each scenario requires you to know precisely what data you collect, where it lives, why you're processing it, how long you retain it, and who else has access to it. That's your organization’s ROPA.
The ROPA-Consent Governance Connection
Here's the insight that shapes the Consent Manager architecture: you cannot effectively manage consent collection without comprehensive records of processing activities.
When a customer gives consent for "processing my PAN card details for credit assessment," the consent manager needs to know:
- What specific data points are collected (PAN number, name, mobile number, address)
- Which systems process this data (credit decisioning system, core banking service)
- What is the exact processing purpose (credit eligibility assessment, not marketing)
- How long the data persists (11 years per PMLA requirements, linked to the loan lifecycle)
- Who else accesses it (credit bureau for verification, auditors for compliance)
Every data point in this list comes from your ROPA. Without it, consent becomes a hollow checkbox, collected but not operationalized.
Building Your ROPA: Lessons from India's Digital Transformation
- Start with Business Processes, Not Compliance
In our work with 200 of India’s largest enterprises, from the largest stockbroker to major private banks, we've found that the best processing records emerge from mapping actual business workflows, not filling out compliance templates.
Take customer onboarding in lending. The business process is:
i. Customer submits a loan application with PII
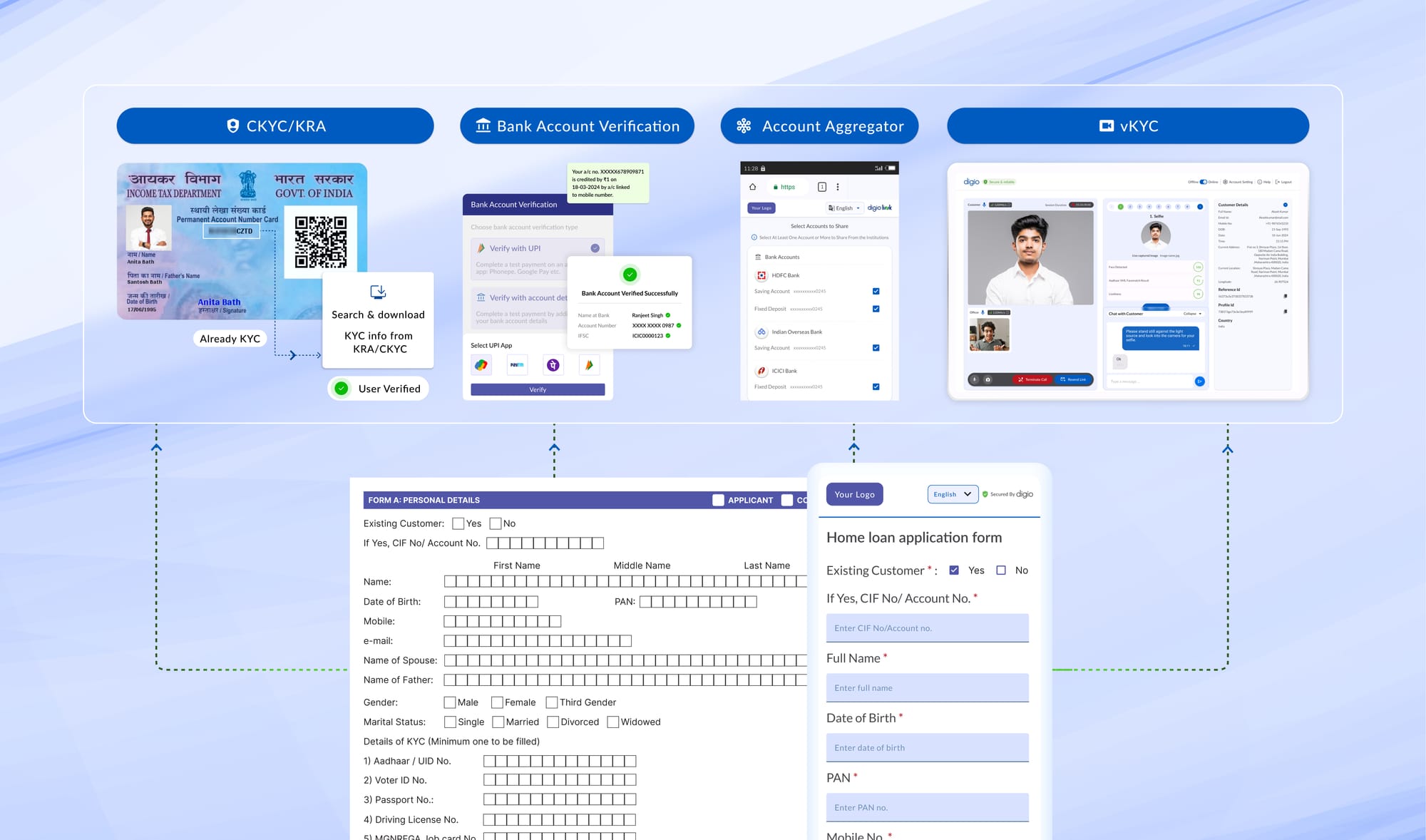
ii. System performs instant eKYC via Aadhaar
iii. The credit bureau check retrieves the credit history
iv. Video KYC captures live verification
v. Document OCR extracts data from uploaded documents
vi. Risk engine processes all data points for decisioning
vii. eNACH setup authorizes recurring EMI debits
viii. Loan disbursement triggers transaction records
ix. Servicing begins with ongoing payment processing
Each step generates specific data processing that must be documented.
When you map ROPA to business processes, the exercise becomes intuitive rather than burdensome.
- Define Your Role with Precision
DPDPA's Data Fiduciary vs. Data Processor distinction is simpler than GDPR's controller-processor framework, but no less important.
For instance, at Digio, we operate as:
- Data Processor when a bank uses our eSign API and controls what documents get signed and why
- Data Fiduciary, when we determine how to verify document authenticity using our ML models
- Both simultaneously in different aspects of the same transaction
This nuance matters intensely under DPDPA Section 8(4), which makes Fiduciaries accountable for Processor failures. Document these relationships explicitly. Your ROPA must document this relationship clarity for every processing activity.
- Capture Data with Business Relevance
Here's what processing documentation should possibly include:
i) Processing Activity Name: Not generic ("Customer Data Management") but specific ("Video KYC Verification for Account Opening"). This precision makes operationalization possible.
ii) Data Principal Categories: Prospective customers, existing customers, guarantors, nominees, employees, vendor representatives. Each category triggers different obligations. Under DPDPA Section 9, children require parental consent. Your ROPA must flag age-sensitive processing.
iii) Personal Data Categories Structure these practically:
- Identity data (PAN, Aadhaar, passport)
- Financial data (bank accounts, income, credit history)
- Biometric data (facial captures for face matching, fingerprints for eKYC)
- Behavioral data (transaction patterns, browsing history)
- Communication data (phone, email, physical address)
iv) Lawful Purpose and Processing Basis: DPDPA primarily relies on consent (Section 6), with specific exemptions under Section 7. Your ROPA must specify:
For Consent-Based Processing:
- The exact purpose communicated to Data Principals
- How consent was obtained (website/mobile app opt-in via consent manager)
- Whether consent was unbundled (separate consent for credit check vs. marketing)
- Consent renewal mechanisms for long-term processing
For Section 7 Exemptions:
- Voluntary data provision by the Data Principal
- Performance of employment or service contract
- Compliance with legal obligations (KYC under PMLA, tax reporting)
- Medical emergency or public health response
- Court orders or government functions
v) Data Retention PeriodsSection 8(5) mandates erasure once purpose is accomplished. Your ROPA must justify every retention period with a business or legal rationale.
Banking example: KYC documents must be retained for 11 years after account closure (PMLA requirements). But marketing data collected with consent should be erased within 2 years of customer inactivity unless fresh consent is obtained.
vi) Cross-Border Data Transfers Section 16 empowers the Central Government to restrict transfers to specific countries. Until notifications emerge, document every international transfer:
- Destination country and specific recipients
- Transfer mechanism (Aadhaar data never leaves India as per UIDAI regulations)
- Security safeguards (encryption standards, access controls)
- Contractual protections with foreign processors
When we use cloud infrastructure, our ROPA specifies data residency commitments (India region), encryption at rest and in transit, and contractual liability for security failures.
vii) Technical and Organizational Measures Section 8(6) requires "reasonable security safeguards." Document your security posture comprehensively:
- Encryption (AES-256 at rest, TLS 1.3 in transit)
- Access controls (role-based access, MFA for privileged users)
- Pseudonymization techniques (hashing PAN numbers, tokenizing Aadhaar)
- Logging and monitoring (audit trails for all data access)
- Incident response (detection mechanisms, escalation protocols)
- Vendor security assessments (third-party audit reports, SLAs)
Map these to recognized standards like ISO 27001, which adds credibility during regulatory scrutiny.
Link ROPA to Broader Privacy Operations
Processing records should interconnect with:
- Consent Management: CoTrust pulls processing purposes from ROPA to generate consent notices
- DSR Handling: When Data Principals request erasure, ROPA identifies all systems containing their data
- Breach Response: ROPA documents data sensitivity levels, guiding incident severity assessment
- Vendor Management: ROPA identifies all Data Processors, triggering contract and security reviews
- Privacy Notices: Public-facing notices derive directly from ROPA documentation
This systems thinking transforms ROPA from static documentation to operational infrastructure in the DPDP mandate.
CoTrust's Role: Operationalization of the ROPA
With CoTrust, we're building on Digio's core insight: trust infrastructure must be both robust and invisible. Our Consent Governance Platform builds on a comprehensive ROPA as its foundation:
1) Purpose-Granular Consent: CoTrust enables separate consent requests for each processing purpose documented in your ROPA. When a banking customer applies for a loan, they see distinct consent requests for: (1) Credit assessment, (2) Credit bureau reporting, (3) Product recommendations, (4) Marketing communications, each linked to specific processing activities.
2) Consent-Processing Linkage: Every consent artifact in CoTrust maps to processing activities in your ROPA. When consent is withdrawn, the platform automatically identifies all affected systems and triggers appropriate data handling workflows.
3) Audit Trail Integration: CoTrust maintains immutable logs of all consent actions: collection, modification, renewal, withdrawal. These logs connect directly to processing documentation, enabling you to demonstrate purpose limitation compliance.
4) Multi-Language Support: DPDPA requires consent in languages that Data Principals understand. CoTrust supports 22 Indian languages, ensuring consent notices reflect processing purposes accurately across linguistic contexts.
5) Real-Time Compliance Dashboard: CoTrust provides filterable views of consent status across geographies, purposes, and Data Principal segments, all organized around processing activities you've documented in ROPA.
The integration is bidirectional: ROPA informs consent management, and consent actions generate processing events that must be documented. This closed loop ensures operational compliance, not paper compliance.
Looking Ahead: DPDPA's Evolving Landscape
While the Data Protection Board is still being constituted and rules are emerging, certain realities are evident:
1) Documentation Will Be Central to Enforcement: Section 33's penalty structure of up to ₹250 crores for serious breaches makes processing documentation your primary defense. Organizations that can demonstrate systematic compliance through comprehensive ROPA will fare significantly better in enforcement actions than those scrambling post-facto.
2) Algorithmic Accountability: Indian organizations that deploy AI/ML systems at scale, processing documentation, must evolve to capture model governance, training data provenance, bias assessments, and automated decision-making safeguards.
3) Children's Data Protection Will Demand Enhanced Documentation: Sections 9 and 10's requirements around parental consent and behavioral monitoring prohibition will require ROPA entries explicitly flagging age-sensitive processing.
4) Cross-Border Transfer Notifications Will Arrive: Section 16 grants government power to restrict international transfers. Organizations with comprehensive ROPA documenting all cross-border flows can respond rapidly when notifications emerge. Those discovering transfer relationships mid-crisis will face operational disruption.
5) Consent Manager Registration Will Clarify Requirements: As the Data Protection Board registers Consent Managers like CoTrust, operational standards will crystallize. Organizations that have already built strong ROPA foundations will integrate these standards seamlessly.
Your next 6 months in Data Privacy
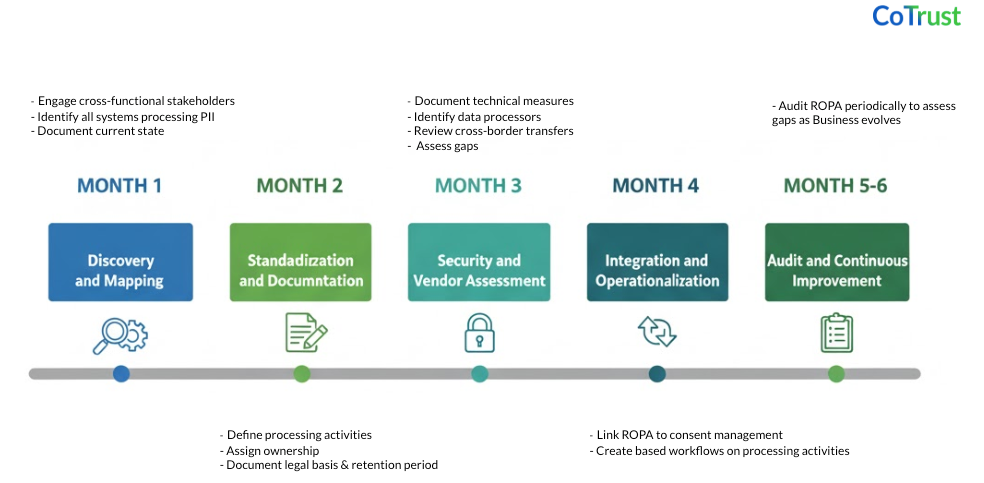
Throughout this journey, remember that ROPA is not a compliance mandate; it's an operational necessity. Every organization processing personal data needs to know what data it holds, why it holds it, and how it protects it. DPDPA simply makes explicit what responsible organizations already practice.
Conclusion: Building Trust Through Transparency
At Digio, we've learned that India's digital transformation depends on trust. Trust that signatures are legally binding. Trust that identities are properly verified. Trust that payment mandates are securely authorized. And now, trust that personal data is processed responsibly.
Records of Processing Activities are the foundation of that trust. They're the documentation that transforms abstract privacy commitments into operational reality. They're the knowledge infrastructure that enables effective consent management through platforms like CoTrust. Every processing activity is mapped. Every consent artifact is traceable. Every data flow is understood. This isn't compliance for its own sake; it's how we operate.
DPDPA compliance isn't a destination; it's a practice. And like all practices, it begins with understanding where you are. That understanding starts with comprehensive Records of Processing Activities.
You can start with the ROPA process by referring to our sample template.
CoTrust is preparing for registration as a Consent Manager with India's Data Protection Board. Built by Digio, a leader in India's digital trust infrastructure, CoTrust brings the same operational rigor to consent management that has powered millions of digital transactions across banking, fintech, telecom, and beyond.
To learn more about how CoTrust can operationalize your DPDPA compliance journey, beginning with ROPA documentation support, visit digio.in/co-trust
Read more Blogs
Digitally transform business operations with Digio!
Try first. Subscribe later.
Boost your legal ops efficiency by 80%
Learn how Digio can enhance your business productivity
Get 1-on-1 business use case solutioning
Speak with our business consultants to get a solution walkthrough for your business requirement
Test the APIs
Let your development team test our API suite to understand configurability and product integration
Subscribe
Get the best in industry commercials for your business usecase