Insurance KYC: Decoding IRDAI AML/CFT Guidelines
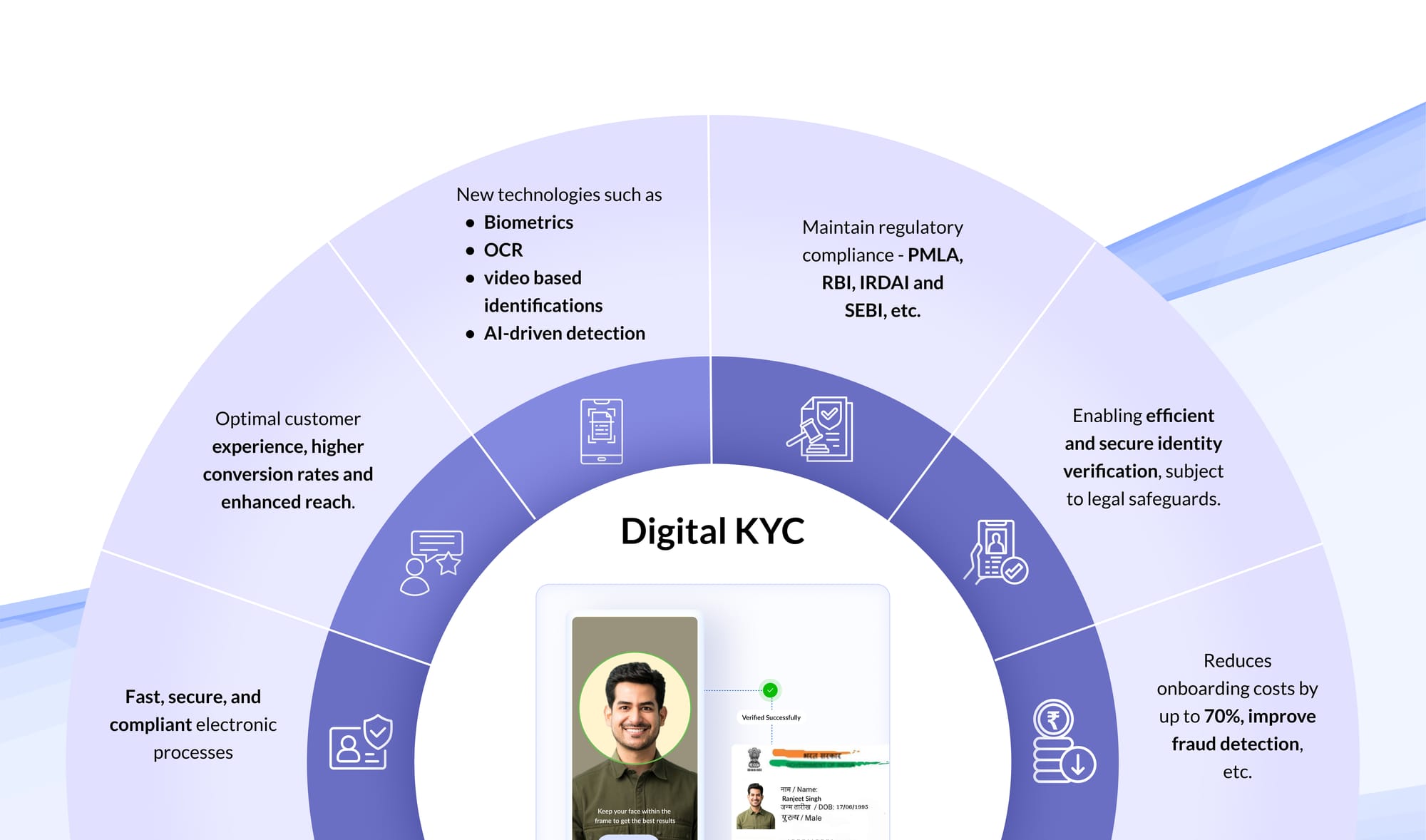
To ensure that insurers accurately verify the true identity of their customers, IRDAI has allowed insurers to use a wide range of Know Your Customer (KYC) methods.
The Indian insurance sector is on a remarkable upswing, with projections from the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) indicating a surge to $222 billion by 2026, outshining countries such as Gеrmany, Canada, Italy, and South Korea.
However, with widening insurance coverage and a mushrooming customer base, the insurance sector inadvertently becomes vulnerable to being used as a front for financial crimes such as money laundering.
To mitigate the risk of money laundering through insurance products, IRDAI has rolled out comprehensive guidelines. Let’s take a deep dive into some of the key sections of these guidelines that all insurance companies in India must comply with.
Decoding IRDAI’s AML/CFT Guidelines for KYC
Section 10.1: KYC Norms
To ensure that insurers accurately verify the true identity of their customers, IRDAI has allowed insurers to use a wide range of Know Your Customer (KYC) methods.
These methods include Aadhaar-based authentication, digital KYC, Video Based Identification Process (VBIP), Central KYC Records Registry (CKYCR) identifiers, and Officially Valid Documents (OVDs). Additionally, for transactions exceeding ₹50,000 annually, IRDAI mandates insurers to obtain the PAN or Form 60 of the applicant.
This framework not only offers insurers flexibility in document submission but also the liberty to employ their preferred Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems for documentation.
Section 10.2: Client Due Diligence (CDD)
IRDAI mandates insurers to meticulously verify the identity of new clients using valid KYC documents. For existing customers, insurers have to regularly update their customers’ KYC details through re-verification.
Sections 11 and 12: Simplified and Enhanced Due Diligence
1) Simplified Due Diligence (SDD)
This approach is tailored for lower-risk scenarios, specifically for insurance policies where the annual premium is Rs 10,000 or less.
SDD streamlines the verification process, reducing the compliance burden in cases with a lower probability of money laundering or terrorist financing risks.
2) Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
EDD is mandated for situations involving higher risks, such as complex transactions or customers with perceivable higher risk profiles.
This rigorous process involves a thorough examination of the customer’s identity, their financial standing, and the origin of their funds.
Section 13: Sharing KYC Information with CKYCR
Insurers are required to retrieve and maintain up-to-date KYC records from the Central KYC Registry (CKYCR), especially when their customers provide a KYC identifier. If the KYC identifier is absent or unavailable, insurers are mandated to record the information in a prescribed format.
IRDAI also mandates that KYC details, including Aadhaar verification data, must be filed with CKYCR within 10 days of establishing a client relationship. Furthermore, periodic updates to KYC records are mandated to ensure compliance with current Customer Due Diligence (CDD) standards.
Section 14: Reliance on Third-Party KYC
Section 14 permits insurers to seek the help of third parties for their customers’ KYC. However, the ultimate responsibility for CDD and EDD solely rests with the insurer.
With third parties, insurers must obtain valid KYC documents from the third party within two days of initiating an account-based relationship, or within fifteen days if the third party belongs to the same financial group.
Section 15: Risk Assessment/Categorization
Insurers must consider sector-specific and country-specific vulnerabilities, tailoring their internal risk assessments to their size, presence, and complexity.
Risk categorization mandates insurers to classify their customers into high or low-risk categories based on individual profiles and product types.
Low-risk individuals can include salaried employees, those from lower economic strata, government entities, or regulated bodies, generally requiring basic identity and location verification. Conversely, high-risk profiles, such as non-residents, high-net-worth individuals, NGOs, trusts, companies with close family ownership, and politically exposed persons, demand enhanced due diligence, KYC, and underwriting procedures.
Section 21: Record-Keeping
Insurers are mandated to maintain records of client identity verification for a period of five years from the insurance transaction date or the end of the business relationship. Insurers should ensure that the first 8 digits of the Aadhaar number are properly or appropriately masked. At no point in time, more than last four digits of the Aadhaar number of any individual should be stored by the insurers in physical or digital form.
With Digio’s Aadhaar masking solutions, you can instantly mask Aadhaar images during document capture or ensure compliance by batch masking images stored in document management servers, seamlessly integrating our APIs and SDKs into applications for on-premise or cloud use.
IRDAI has allowed insurers to keep these records in both electronic and physical forms. When using third-party services, insurers must ensure controlled access to data systems, monitored electronic networks, and adherence to data transmission and encryption protocols.
Complying with IRDAI’s AML/CFT Guidelines
For insurance companies, navigating and adhering to IRDAI’s exhaustive guidelines can become overwhelming at times.
Here is how you can seamlessly adhere to IRDAI’s guidelines:
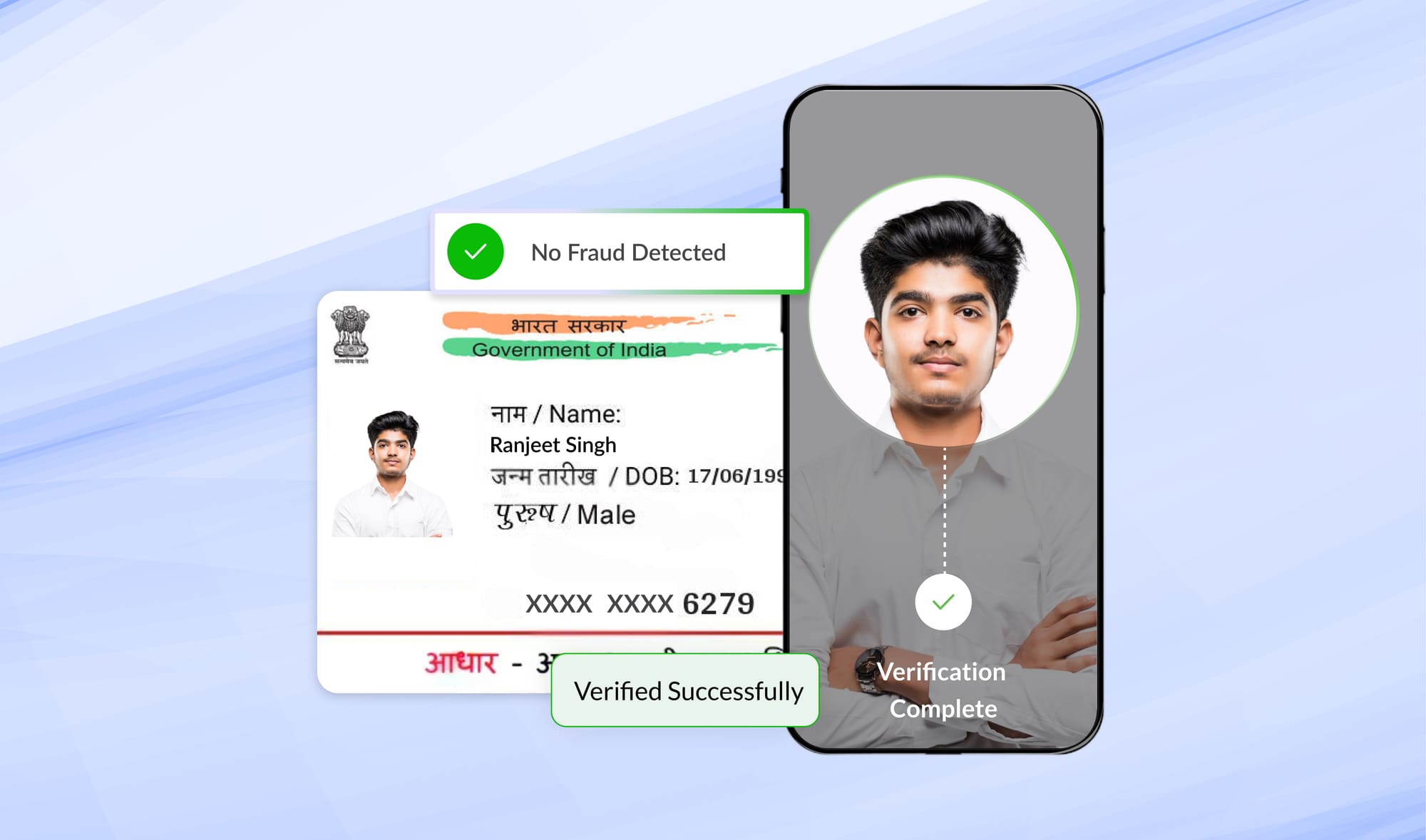
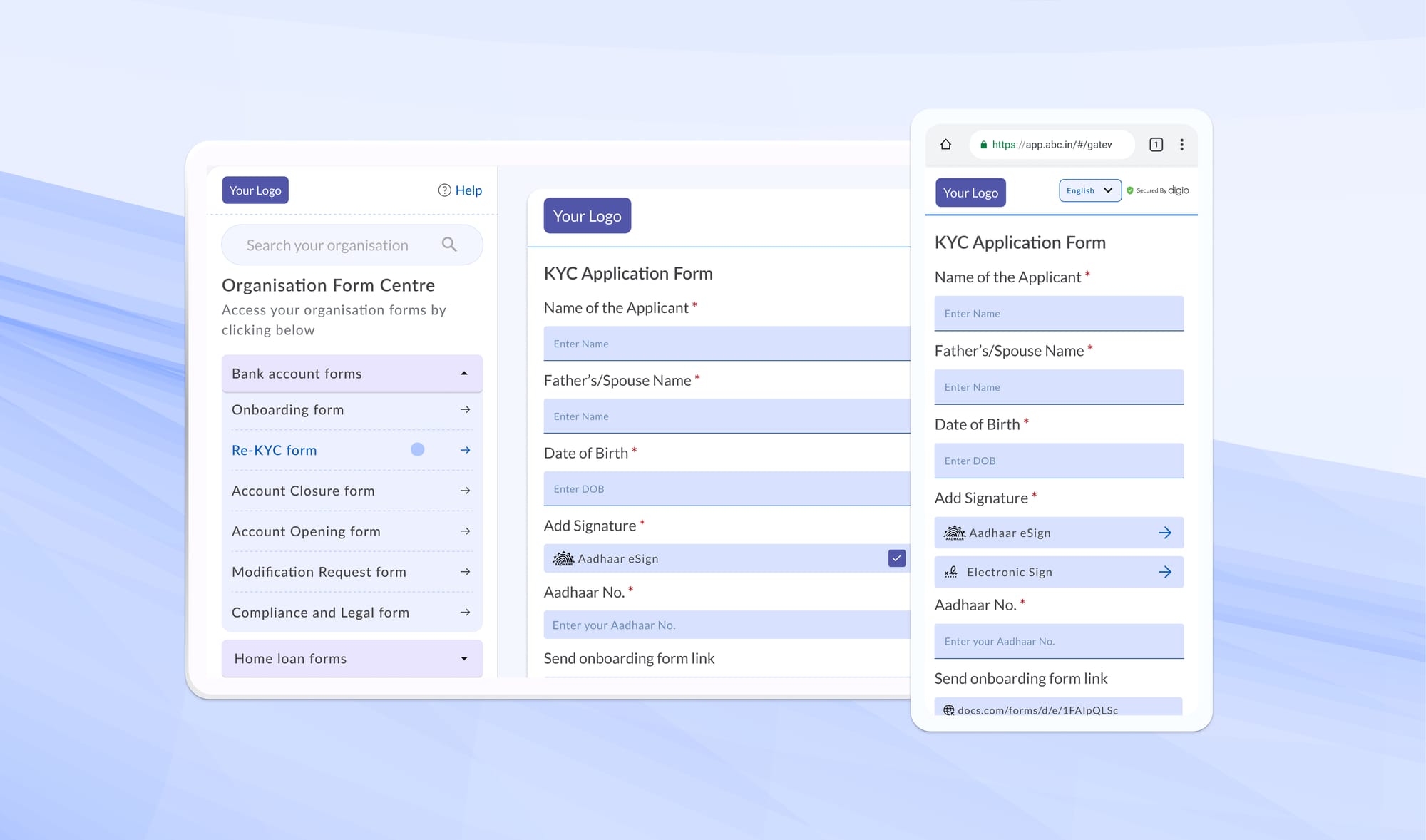
1. Identity Verification
The guidelines mandate the following documents to be collected for KYC purposes:
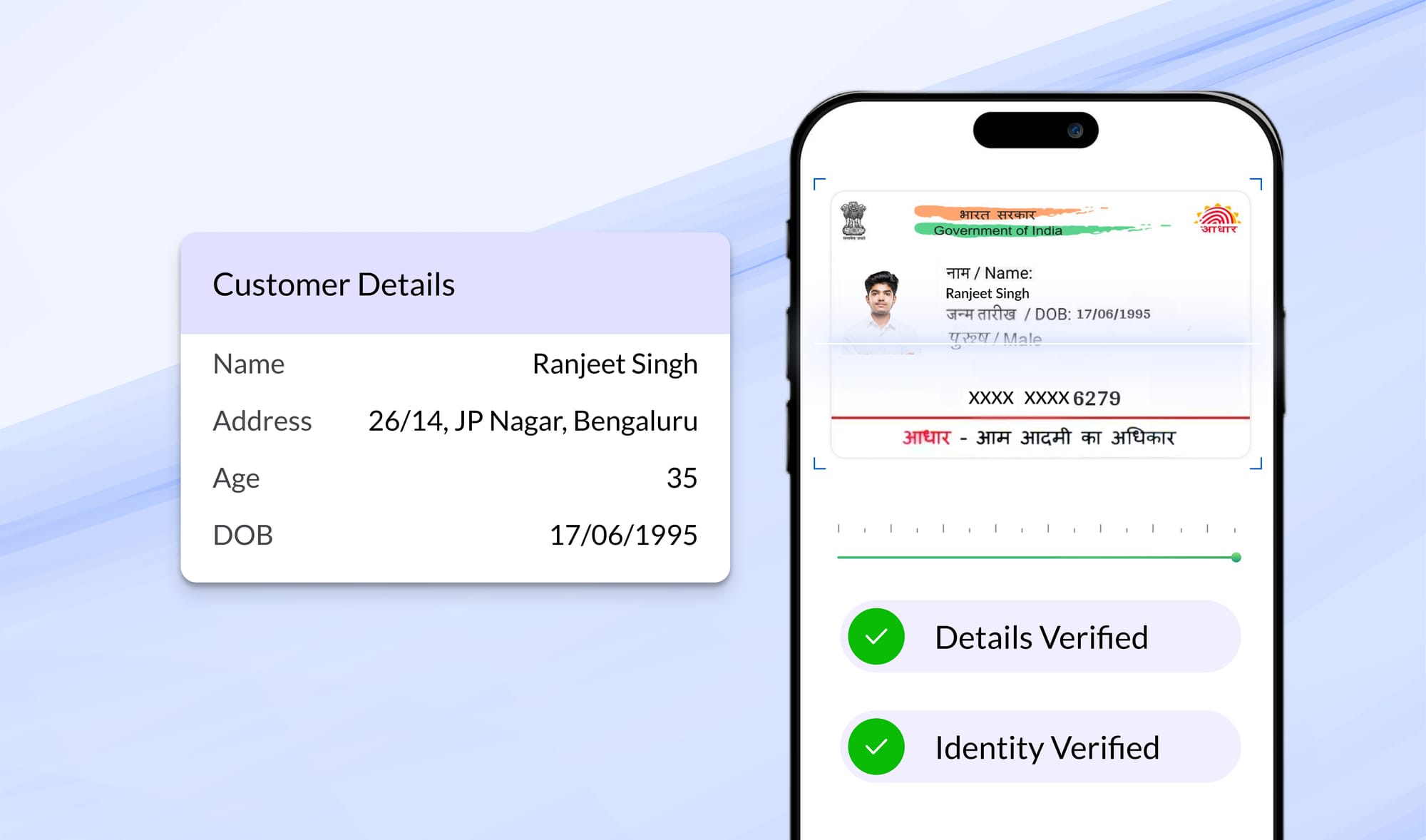
A common challenge that many insurers face is meticulously extracting the correct information from the ID documents submitted by their customers.
This can be done using image-level detection and optical character recognition (OCR). As in case, Digio ID OCR stands out for its spot-on OCR performance and excels in recognizing various identity cards, including Aadhaar, voter ID, driver's license, passport, and more, in image and pdf formats.
The platform also ensures validation and verification through a central database, including text, image, and signature detection, with real-time checks against government databases like CVLKRA, CERSAI, CAMSKRA, NDML, and others. Know more
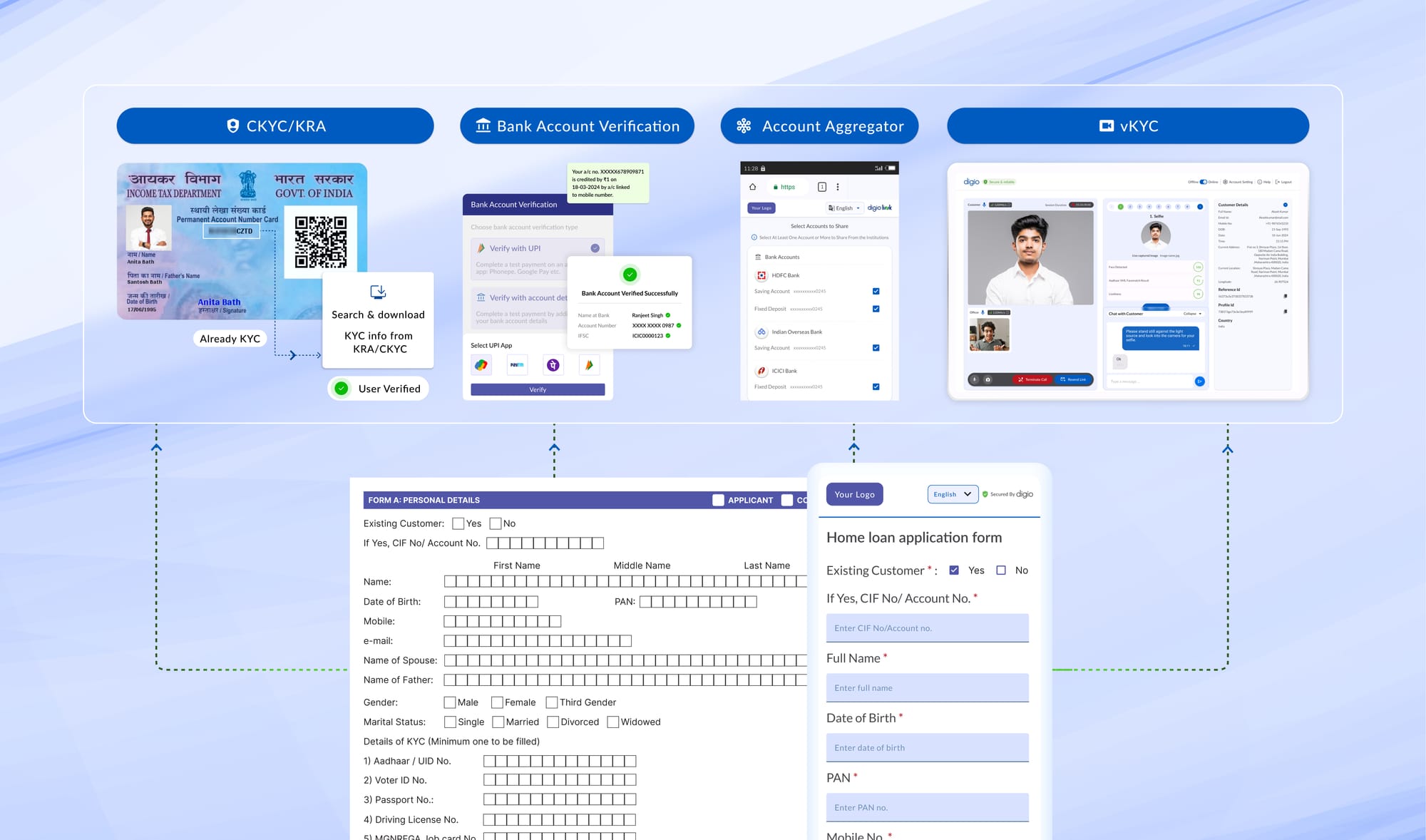
To make the ID verification process foolproof, insurers can also explore KYC solutions with DigiLocker integrations that will allow them to match the ID information with central government databases.
With Digio’s Digilocker Integration, one can access legally binding electronic IDs for verification purposes, as electronic documents from Digilocker are endorsed under Indian laws, as outlined in PMLA guidelines and KYC circulars by the RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, and other central regulators. This simplifies the document retrieval process with single-point authentication, saving valuable time and resources. Know more
The same goes with business KYC, where insurers can accurately verify and validate critical details like GSTIN, PAN, CIN, Director DIN, MSME/Udyog Aadhaar, and FSSAI of non-individual entities using business background verification APIs by Digio.
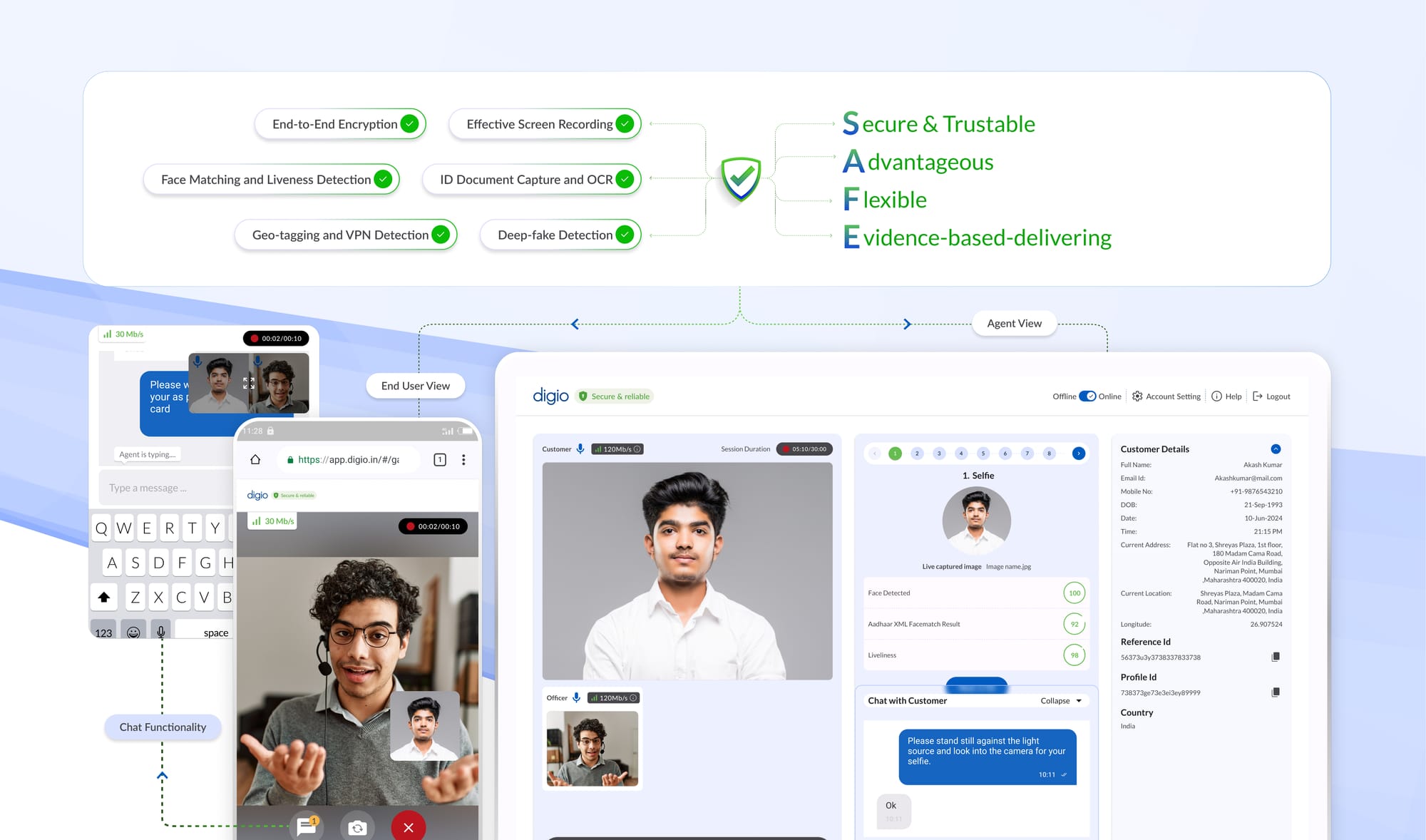
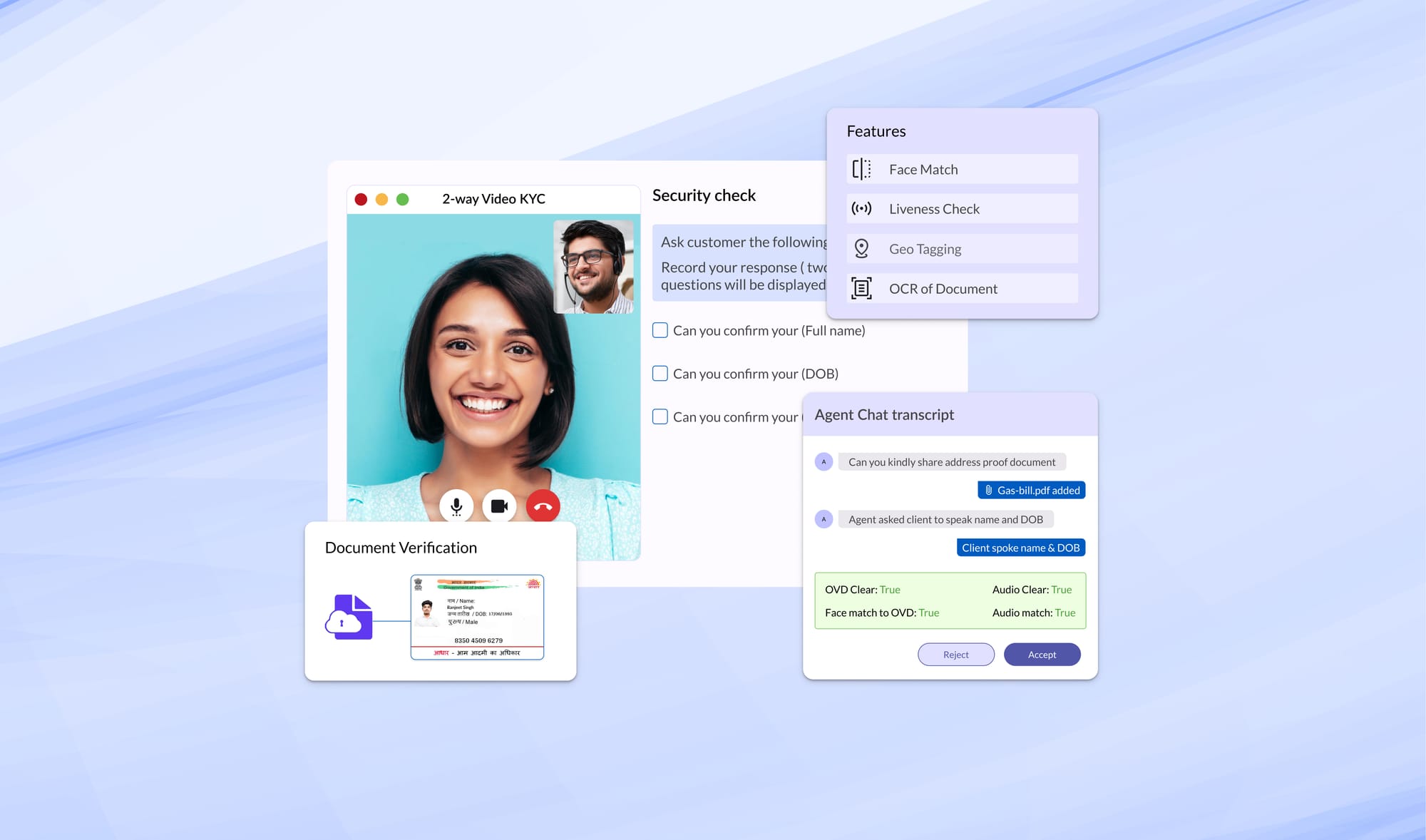
2. Impersonation Checks through Video-Based Identity Process (VBIP)
IRDAI has allowed insurers to conduct live KYC verifications of their customers (either online or in person) through VBIP.
To avoid any ambiguities in the VBIP process, IRDAI has mandated the following:
Clear Live Video Recording
The insurer or an authorized person, while performing the VBIP for KYC, shall record a clear live video of the customer or beneficiary present for identification and obtain the identification information in the form below:
i. Aadhaar authentication, if voluntarily submitted by the customer beneficiary
or
ii. Offline Verification of Aadhaar for identification, if voluntarily submitted by the customer or beneficiary, is subject to the QR code and XML file generated within 3 days of submission
or
iii. Officially valid documents are provided in the following manner:
(1) As digitally signed document of the Officially Valid Documents, issued to DigiLocker by the issuing authority
or
(2) As a clear photograph or scanned copy of the original, Officially Valid Documents, through the eSign mechanism
Special care must be taken to ensure that the video is clear and that both the customer and the insurer’s authorized person are easily recognizable without any face coverings.
Furthermore, IRDAI has also mandated that the video interaction be encrypted and Aadhaar numbers be redacted to avoid any breach of privacy.
Geo-Tagging and Liveness Check
Insurers must capture the live location to confirm their customer's physical presence in India.
Additionally, they must verify that the details in Aadhaar/OVDs match the customer present in the video through liveliness checks to prevent spoofing.
Recording Details
Insurers must trigger their VBIP audio-visual interaction only from their web domain and maintain all logs and official credentials.
Additionally, these VBIP recordings must include GPS coordinates, date, and time while preserving additional details like IP addresses. If the data is located in a third-party location or cloud, ensure it is in India as per guidelines.
Face and Name Matching
Verify that the photograph and details in the Aadhaar/Officially Valid Documents match those of the customer or beneficiary during the Video-Based Identification Process (VBIP). Use available technology, including AI and face-matching technologies, to enhance process integrity and confidentiality.
Support for in-built questionnaire and call summary reports
Vary the sequence and type of questions in video interactions to ensure real-time engagement while preserving call summary reports, activity logs, and credentials securely.
Aligning with IRDAI’s VBIP mandates, Digio’s Video KYC offers high-quality live video interactions for agent-assisted video KYC, self-video KYC with dynamic OTP and voice-to-text analytics, advanced OCR for ID verification during video calls, facial recognition with geotagging, guided UI with multi-user support and access management, call summary reports, in-call chat and file sharing, and roster management with call reminders—almost everything you need to undergo a secured, compliant video KYC to onboard your customers.
3. Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
When it comes to identity verification, merely extracting the information from the customers’ ID documents may not always be sufficient. For foolproof verification, insurers must undertake EDD by re-verifying customers’ identities with their bank account KYC records.
With Digio’s bank verification solutions, insurers can quickly initiate comprehensive bank account verification to ensure the accuracy of the bank account details submitted by the customer. Critical aspects involved are the modes of verification, which need to comply with IRDAI regulations. Compliant verification modes include Penny Drop, Custom Penny Drop, Penniless, Reverse Penny Drop, and UPI VPA Authentication. Provisions for bulk bank a/c verification that is backed by multiple banks registered in India are also valid as per guidelines.
Another aspect involves matching the customer’s name, as per KYC, with the bank records. There’s a need for comprehensive technology to fuzzy check between names as per KYC records and names as per bank records with confidence score allocation to ensure that the right individual is being verified and validated to avail of insurance services.
Digio Bank Verification APIs solves all the above with the best-in-industry latency. With successful implementation, businesses have been able to reduce operational overheads and unleash business productivity.Know more
Recently, IRDAI has also mandated the use of account aggregator services for financial data procurement and sharing within the AA ecosystem. This move is a masterstroke in mainstreaming insurance with other financial products. An account aggregator is an interoperable data-blind consent custodian that helps in sharing financial information between financial institutions based on customer consent. To learn more, please visit Digio Link
Summing Up
By covering critical aspects such as KYC norms, risk assessment, and internal control measures to shield the insurance sector from financial crimes, IRDAI’s AML/CFT guidelines mark a significant step in aligning India's insurance industry with global standards in financial security.
Adhering to these guidelines is not merely a regulatory obligation for insurers but also a fundamental aspect of maintaining customer trust by ensuring the integrity of financial transactions.
To learn how Digio can help you seamlessly comply with IRDAI’s guidelines, please visit https://www.digio.in/#/digi-kyc or get in touch with us at support@digio.in.
Citations:
[1] The Rise of India’s Insurance Industry
[2] IRDAI’s ‘Master Guidelines On Anti Money Laundering/Counter Financing Of Terrorism (AML/CFT)’
Read more Blogs
Digitally transform business operations with Digio!
Try first. Subscribe later.
Boost your legal ops efficiency by 80%
Learn how Digio can enhance your business productivity
Get 1-on-1 business use case solutioning
Speak with our business consultants to get a solution walkthrough for your business requirement
Test the APIs
Let your development team test our API suite to understand configurability and product integration
Subscribe
Get the best in industry commercials for your business usecase